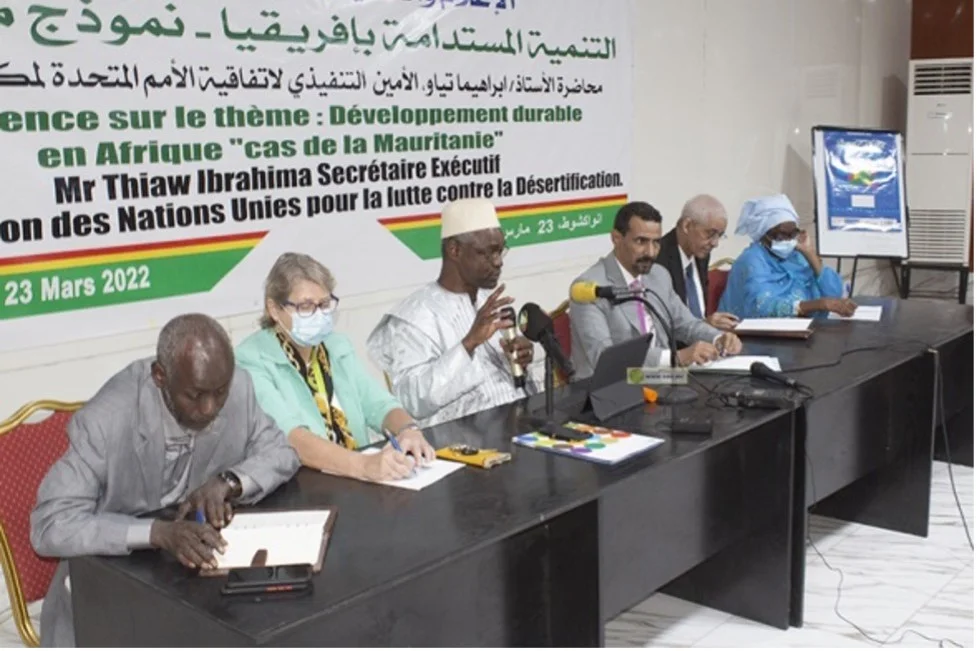
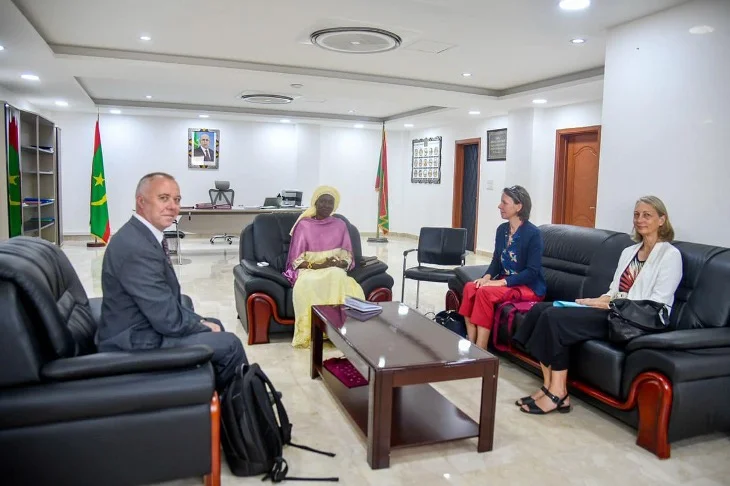
The United Nations in Mauritania

The United Nations in Mauritania consists of 17 resident and non-resident agencies, funds, and programs, all working collaboratively with the government of Mauritania for the country’s development. They contribute to providing support and addressing humanitarian and developmental challenges faced by Mauritania, based on the relative merits of each UN agency and partner non-governmental organizations.
The support of the United Nations system in Mauritania is reflected in the programs and projects implemented by various entities of the United Nations in the country. Through their interventions, the system offers Mauritania a unique set of skills and resources, committed to ensuring more effective, rational, cohesive, and synergized presence, in line with the United Nations reform policy, especially the “Delivering as One” approach.
The United Nations system in Mauritania contributes through its collective efforts to accelerate the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals, taking into account the national priorities of the government of Mauritania. These priorities are outlined in a document titled “Partnership Framework for Sustainable Development,” which serves as the strategic reference framework for coordinated United Nations interventions at the national level.
Strategic Priorities:
- Comprehensive Growth
Result 1: Institutions responsible for economic management develop and implement policies contributing to comprehensive and sustainable growth.
Result 2: The population has access to enhanced livelihoods, decent jobs, increasing economic opportunities, and improved food security.
Result 3: Institutions and communities contribute to sustainable management of natural resources to anticipate, address, and manage the impacts of climate change.
- Human Capital and Essential Social Services
Result 1: Children and youth receive quality education in formal and non-formal systems.
Result 2: Vulnerable populations have access to sufficient and sustainable health and nutrition services, drinking water, basic sanitation, and hygiene.
Result 3: Institutions, civil society, and communities provide better protection against various forms of discrimination, including the consequences of slavery, exploitation, physical, psychological, and sexual violence.
- Governance
Result 1: Democratic institutions operate more transparently and inclusively, expanding the democratic space to improve peaceful coexistence, social cohesion, security, justice system, and prisons become more independent and efficient.
Result 2: Institutions better manage mixed migration flows, provide better protection for refugees, asylum seekers, and vulnerable migrants, prevent their trafficking, and contribute to peaceful coexistence between refugees and host communities.
Result 3: The population benefits from improved access to civil registration.
Result 4: Central and local institutions ensure more efficient and transparent direction and coordination of public policies.
 Algeria
Algeria Bahrain
Bahrain Comoros
Comoros Djibouti
Djibouti Egypt
Egypt Iraq
Iraq Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lebanon
Lebanon Libya
Libya Mauritania
Mauritania Morocco
Morocco Oman
Oman Palestine
Palestine Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Somalia
Somalia Sudan
Sudan Syria
Syria Tunisia
Tunisia UAE
UAE Yemen
Yemen




